Week 4
Comparing different feature detection algorithms
FAST - Features from Accelerated Segment Test [1]
Keypoints Detection
This is the FAST feature detection algorithm with the Non-Maximum Suppression turned on. FAST works by comparing each pixel with it’s neighbours to detect corners. This algorithms will probably not be used because the FAST object in the feature2d module cannot create a descriptor for images.
| PCB1 | PCB2 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Code
def displayFAST(window, image, nms=1):
fast = cv2.FastFeatureDetector_create()
fast.setNonmaxSuppression(nms)
keyPoints = fast.detect(image, None)
corners = image.copy()
corners = cv2.drawKeypoints(image = image, keypoints = keyPoints, outImage = corners, color = (0, 0, 255))
cv2.imwrite('fast.jpg', corners)
cv2.imshow(window, corners)
ORB - Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF [2]
Keypoints Detection
This is a feature detection algorithm created by the developers of opencv. It provides similar features to other patented feature detection algorithms such as SURF or SIFT.
| PCB1 | PCB2 |
|---|---|
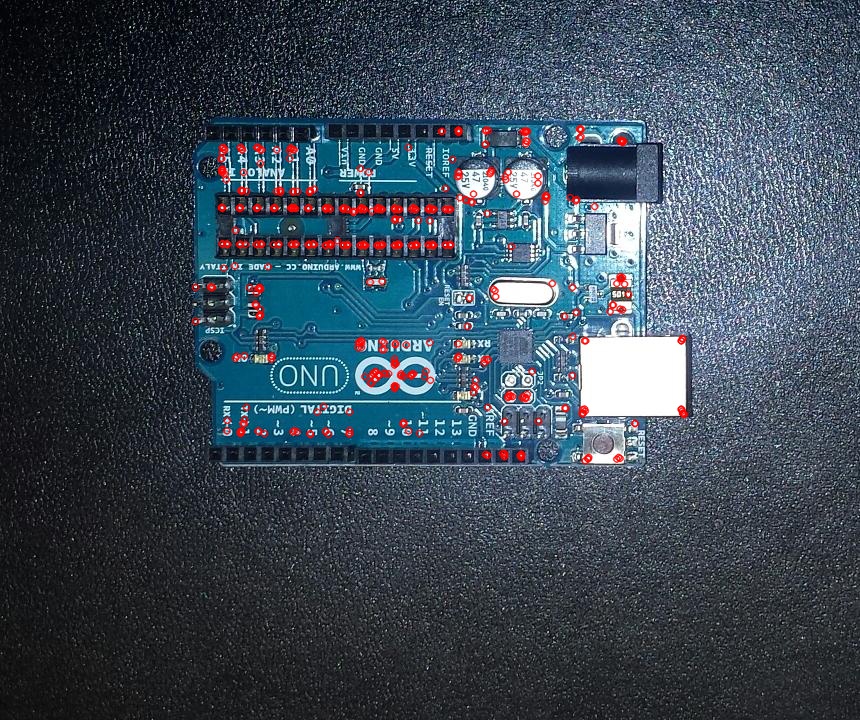 |
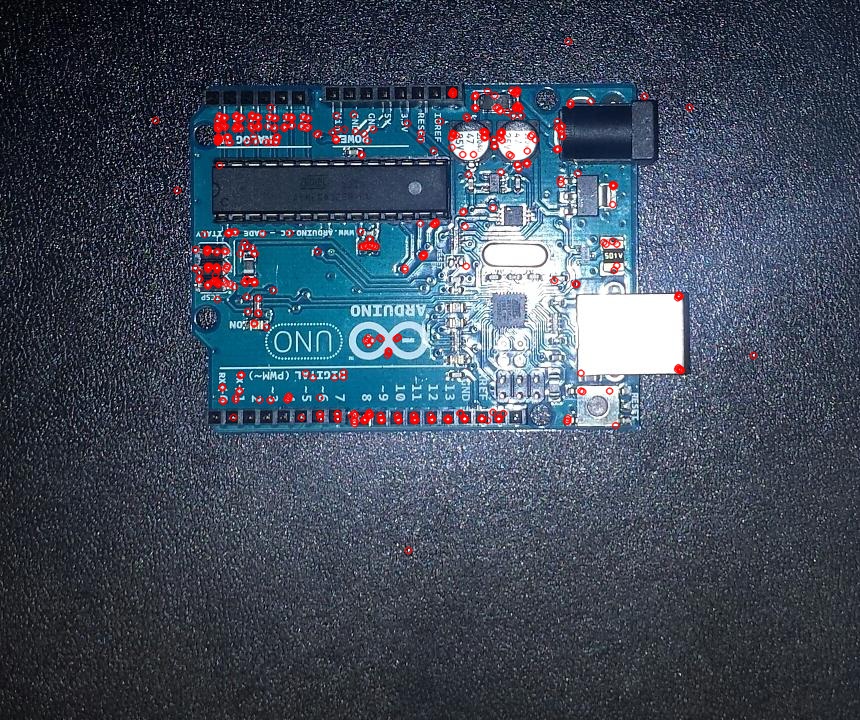 |
Code
def displayORB(window, image):
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
keyPoints = orb.detect(image, None)
keyPoints, descriptor = orb.compute(image, keyPoints)
newImage = image.copy()
newImage = cv2.drawKeypoints(image = image, keypoints = keyPoints, outImage = newImage, color = (0, 0, 255), flags = 0)
cv2.imwrite('orb.jpg', newImage)
cv2.imshow(window, newImage)
Feature Matching
While it doesn’t find as many key features in the images, when combined with a Brute-Force Matching algorithm such as BFMatcher it finds many common features. These are the best 250 matches.
| Common Features using ORB and BFMatcher |
|---|
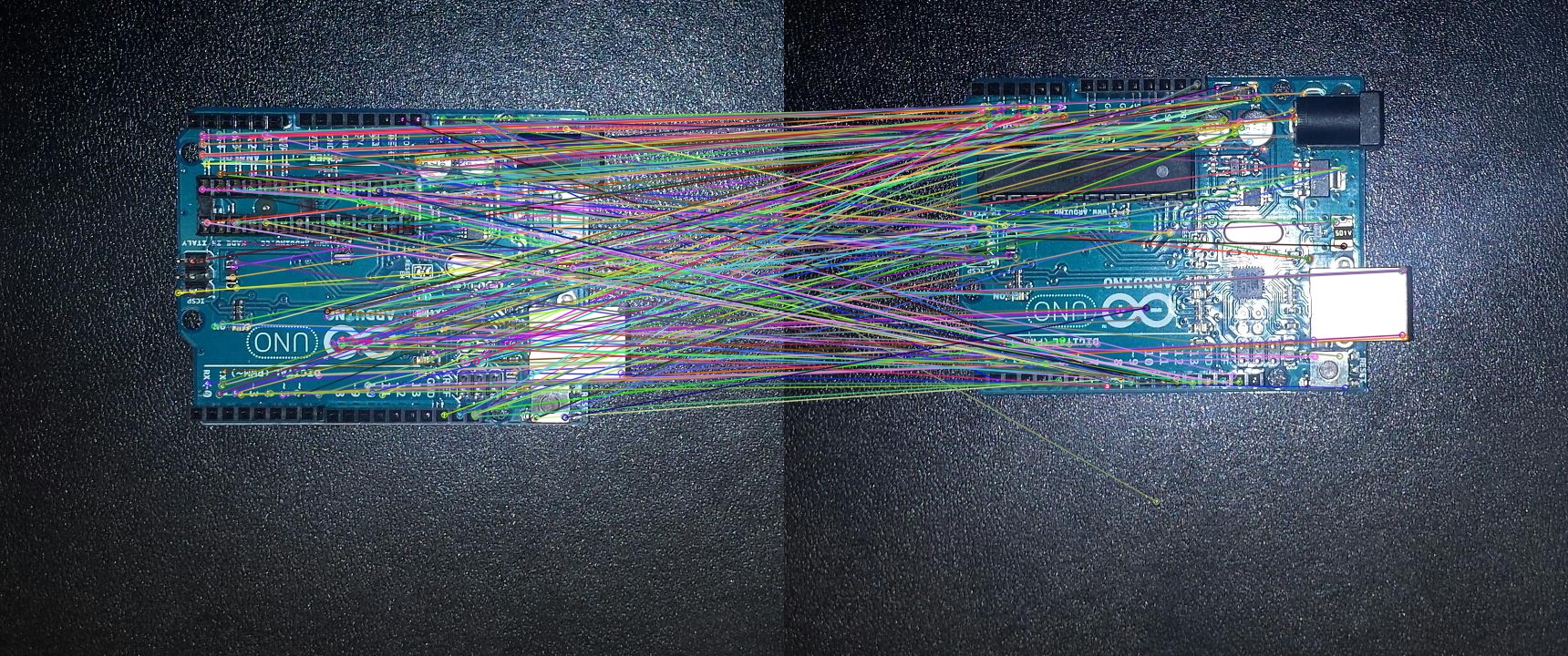 |
Code
def showCommon(window, image1, keyPoints1, desc1, image2, keyPoints2, desc2):
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck = True)
matches = bf.match(desc1, desc2)
matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
matchesImage = image1.copy()
matchesImage = cv2.drawMatches(img1 = image1, keypoints1 = keyPoints1, img2 = image2, keypoints2 = keyPoints2, matches1to2 = matches[:250], outImg = matchesImage, flags=2)
cv2.imwrite(orbFeatures.jpg, matchesImage)
cv2.imshow(window, matchesImage)
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
keyPoints1, desc1 = orb.detectAndCompute(I1, None)
keyPoints2, desc2 = orb.detectAndCompute(I2, None)
showCommon('orbFeatures', I1, keyPoints1, desc1, I2, keyPoints2, desc2)
AKAZE [3]
Keypoints Detection
This is another algorithm for detecting common features. It uses a homography matrix to detect local features.
| PCB1 | PCB2 |
|---|---|
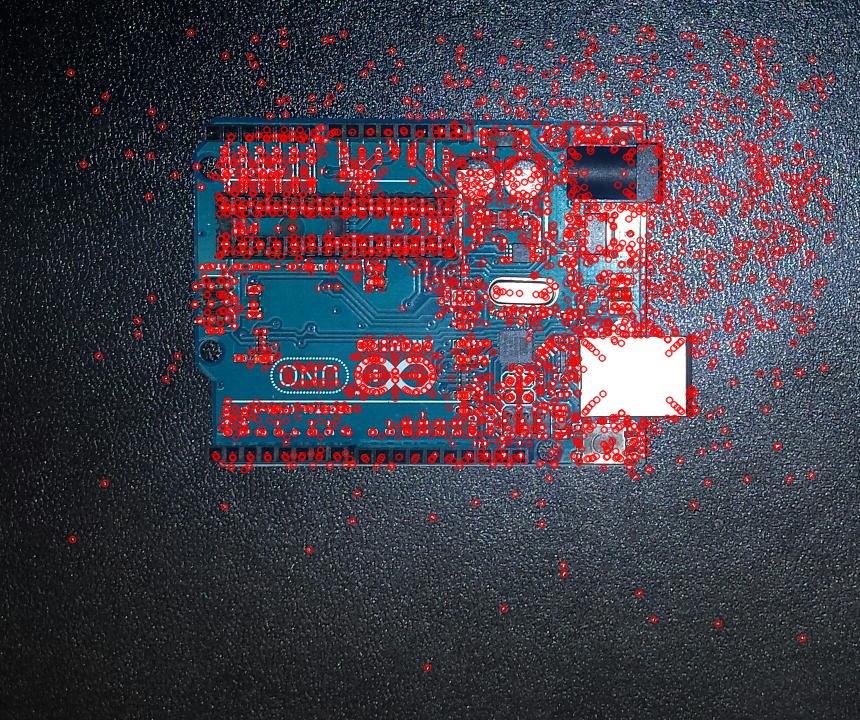 |
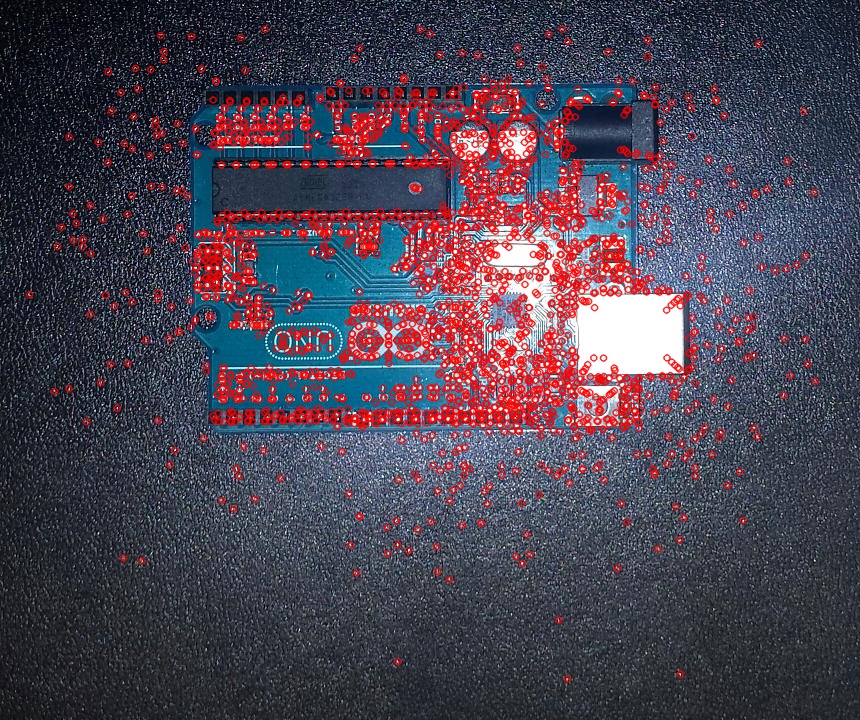 |
Code
def displayAKAZE(window, image):
akaze = cv2.AKAZE_create()
keyPoints = akaze.detect(image, None)
newImage = image.copy()
newImage = cv2.drawKeypoints(image = image, keypoints = keyPoints, outImage = newImage, color = (0, 0, 255), flags = 0)
cv2.imwrite('akaze.jpg', newImage)
cv2.imshow(window, newImage)
By comparing the images using the BFMatching algorithm the folowing 250 best similarities are found.
| Common Features using AKAZE and BFMatcher |
|---|
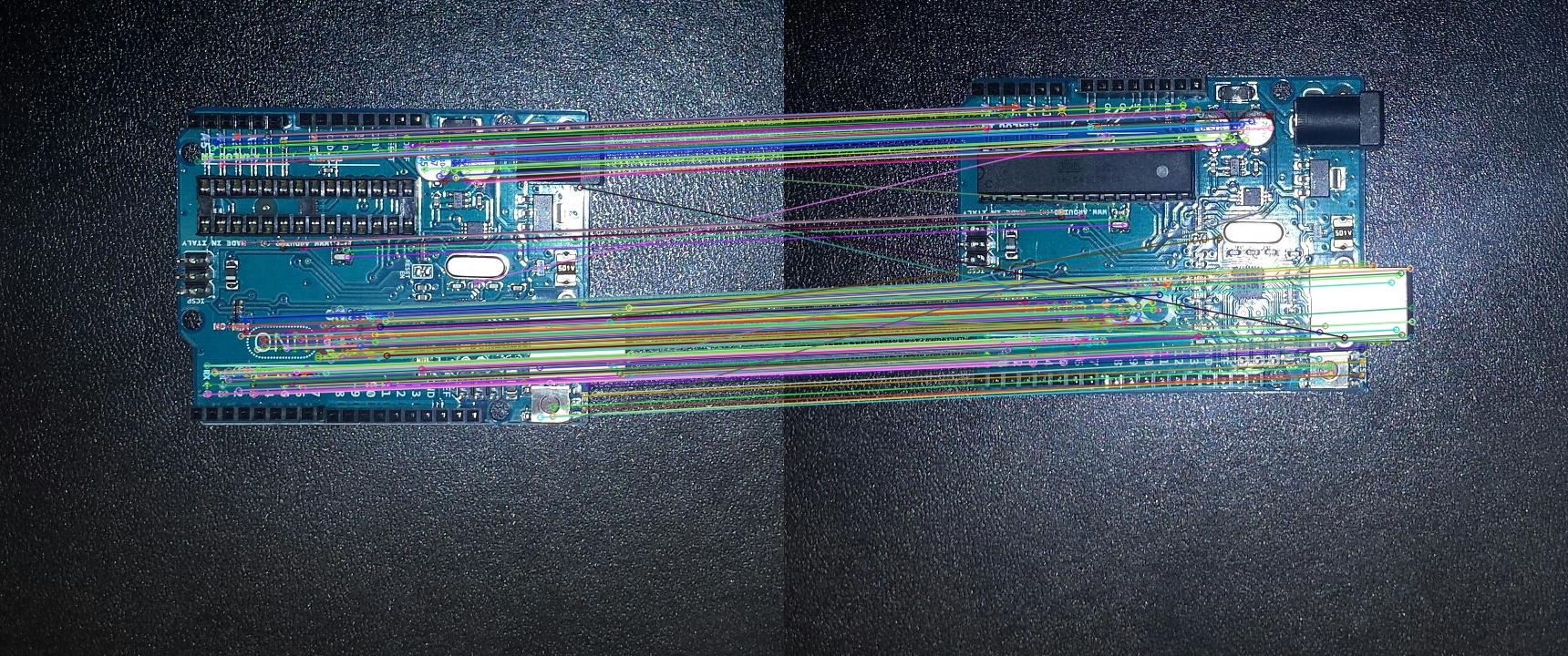 |
Code
def showCommon(window, image1, keyPoints1, desc1, image2, keyPoints2, desc2):
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck = True)
matches = bf.match(desc1, desc2)
matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance)
matchesImage = image1.copy()
matchesImage = cv2.drawMatches(img1 = image1, keypoints1 = keyPoints1, img2 = image2, keypoints2 = keyPoints2, matches1to2 = matches[:250], outImg = matchesImage, flags=2)
cv2.imwrite('akazeFeatures.jpg', matchesImage)
cv2.imshow(window, matchesImage)
akaze = cv2.AKAZE_create()
keyPoints1, desc1 = akaze.detectAndCompute(I1, None)
keyPoints2, desc2 = akaze.detectAndCompute(I2, None)
showCommon('akazeFeatures', I1, keyPoints1, desc1, I2, keyPoints2, desc2)
Comparing the Algorithms
The FAST algorithm seems to detect the most common features but the lack of a descriptor generator makes this method harder to use.
ORB compared to FAST, not only has a compute function for creating descriptors, but it can also compare images that are not in the same orientation. In fact this algorithm uses FAST for feature detection, BRISK for creating the descriptor and it also has an added feature of detecting feature even if they are rotated.
AKAZE works similarly to ORB, with some differences. While AKAZE is slower than ORB, especially for high-resolution images, it provides more correct matches between images[4]. This can be clearly seen in the images above showing the common features between the images.
References:
[1] ‘FAST Algorithm for Corner Detection’, 2014, [Online]. Available: http://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_feature2d/py_fast/py_fast.html. [Accessed: 2017-10-05]
[2] ‘ORB (Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)’, 2014, [Online]. Available: http://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/py_tutorials/py_feature2d/py_orb/py_orb.html#orb. [Accessed: 2017-10-05]
[3] ‘AKAZE local features matching’, 2014, [Online]. Available: http://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/doc/tutorials/features2d/akaze_matching/akaze_matching.html. [Accessed: 2017-10-05]
[4] Daniel R. Roos, Elcio H. Shiguemori and Ana Carolina Lorena, ‘Comparing ORB and AKAZE for visual odometry of unmanned aerial vehicles’, 2015